
Wind turbines or windmills are incredible machines that convert the kinetic energy of wind and ferry it to electrical energy. The process of generating energy free from wind relies upon the aerodynamic motion of rotor blades to spin generators to produce power. How does windmill electricity work exactly? Let's look at it step by step, reviewing the aerodynamics of wind turbines, their major components, innovations, and even how wind industry leaders, KP Energy, generate and improve the growth of renewable energy from wind.
The wind is indirectly powered by the sun. The sun heats the Earth inconsistently and causes the air to move, which is what we know as wind. It is this principle that allows windmill energy changes.
Fans work by using electricity to create wind. Wind turbines operate using wind to electricity process mechanisms to create energy. Wind moves and rotates blades, which in turn, moves and rotate a shaft, which powers a generator.
Ancient windmills were used for grind grain and pumping water. The process of producing wind energy has transitioned to wind energy for electricity production, with new designs and new materials.
Introduction of horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWTs)
Development of tall towers for greater wind capture
Digital sensors for real-time monitoring
Segmented blades and modular designs for transport efficiency
Smart wind turbines with IoT-enabled systems
Carbon fiber composite blades
Onsite assembly using 3D printing
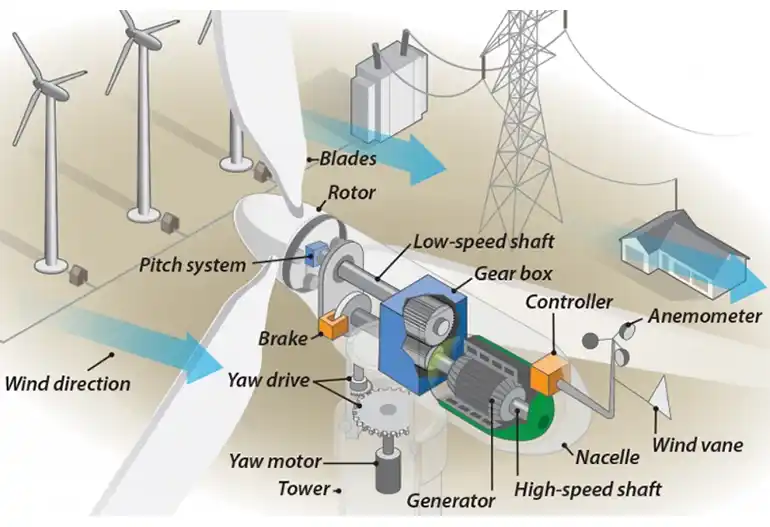
To understand how wind turbines work and to examine their components and functions.
Designed with precision, blades use the aerodynamics of wind turbines to create lift and drag. These forces rotate the rotor, initiating energy conversion.
Blades are mounted on the rotor, which is connected to the hub, a central component that transmits mechanical energy to the drivetrain.
Located behind the rotor, the nacelle contains:
Drivetrain and Gearbox: This converts low-speed rotation from the rotor into high-speed rotation suitable for generating electricity.
Generator: The working principle of wind turbine generation lies here. The generator transforms mechanical motion into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction.
Yaw System: This system rotates the nacelle to face prevailing wind directions for optimal efficiency.
Anemometer and Wind Vane: This equipment is used to measure wind speed and direction to calculate turbine positioning and safety systems.
Braking and Control System: Governs safe shutdown in high winds and regulates the functions of the turbine.
Tower: A tower pushes the rotor and blades to areas of higher wind speed. The tower must be able to withstand the dynamic forces.
Anchors the entire turbine structure, ensuring stability across various terrains.
The wind to electricity process is a sequential transformation of energy:
Wind hits the blades, that generates a rotational force through aerodynamic lift.
Blades spin the rotor, transferring motion to the shaft.
The drivetrain increases rotational speed using a gearbox.
The generator converts mechanical energy into AC electricity
Then the electrical power reaches a transformer, increased in voltage, and is sent into the grid.
This simplified wind power electricity generation system is making today's turbines more efficient and scalable.
The most commonly used in utility scale wind farms because of their efficiency capturing wind from consistent directions.
Used in urban or niche applications where wind is turbulent or from any direction.
Onshore is easier to install and maintain.
Offshore turbines capture more strong and consistent winds but are expensive.
Wind power output is proportional to the cube of wind speed, small increases yield big returns.
With longer blades and taller towers, we can access faster winds, which ultimately improves energy capture.
Chilled, dense air performs better. Altitude and temperature become key factors.
These two metrics tell us how well a turbine performs over time compared to its absolute peak performance.
Lightweight and strong materials, such as carbon fibre, make longer and larger blades that require less wind to start working at higher efficiencies.
Enhances the ability to ship blades to customers, builds larger turbines, and have more megawatts of electricity from the wind.
Includes nacelle components and turbine bases. Having less waste in the process and reducing complexity in the logistics.
Zero emissions during operation
No water consumption
Minimal land degradation
Reduced dependency on fossil fuels
Job creation in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance
Low marginal cost of power after installation
Diversifies the grid and stabilizes energy prices over the long term.
At KP Energy Limited, we are deeply invested in advancing renewable energy from wind through:
Development of utility-scale wind farms
Turnkey EPC services
Wind-solar hybrid projects
Site-specific wind resource analysis
Our commitment to engineering excellence and sustainability places us at the forefront of India’s clean energy transformation.

Choose KP Energy as your trusted renewable energy partner. Reach out today and take the first step toward a greener tomorrow.
The modern windmill has evolved into the advanced framework that supports energy solutions to global issues and has no longer remained as a basic farm fixture. The science of windmill energy conversion started out simple enough, and there are now cutting-edge advancements in the field. The obvious wind turbine generation work has changed, as the future of wind power shared electrical energy will expand with the help of innovators like KP Energy, paving the way for a sustainable future.
Q1. How do windmills generate electricity?
A. Wind pushes on blades, which spin a shaft on a generator. The generator creates electricity through electromagnetic induction.
Q2. What basic principles enable a wind turbine to create electricity?
A. Wind provides lift and drag on blades, causing them to rotate. The blades rotate at some speed to drive a generator to produce AC electricity.
Q3. What are the basic components of wind turbines?
A. The basic components are-Blades, rotor, hub, nacelle, tower and the foundation.
Q4. What kind of generators do windmills use?
A. Most turbines use induction or synchronous AC generators depending on grid impedance criteria and variability of the wind.