Wind energy has become one of the most promising renewable energy resources and now contributes a significant share of global electricity generation. Wind turbine performance, in particular, is strongly influenced and enhanced by advanced wind energy control systems, which play a critical role in improving efficiency, ensuring worker safety, and extending asset life. These control systems continuously monitor and regulate key operational parameters such as rotor speed and power output, while also reflecting the technologies and best practices that define modern wind energy systems.
Over the past thirty years, a multitude of wind turbine control systems have come on the market as development of technologies to enhance energy capture or protect your equipment from extreme environmental conditions became more sophisticated. Therefore, it is crucial for any wind energy installer, operator, or maintainer to have a basic understanding of turbine control systems because the level of performance can affect the efficiency of turbine projects, reliability to the end-user, and overall value of turbine projects.
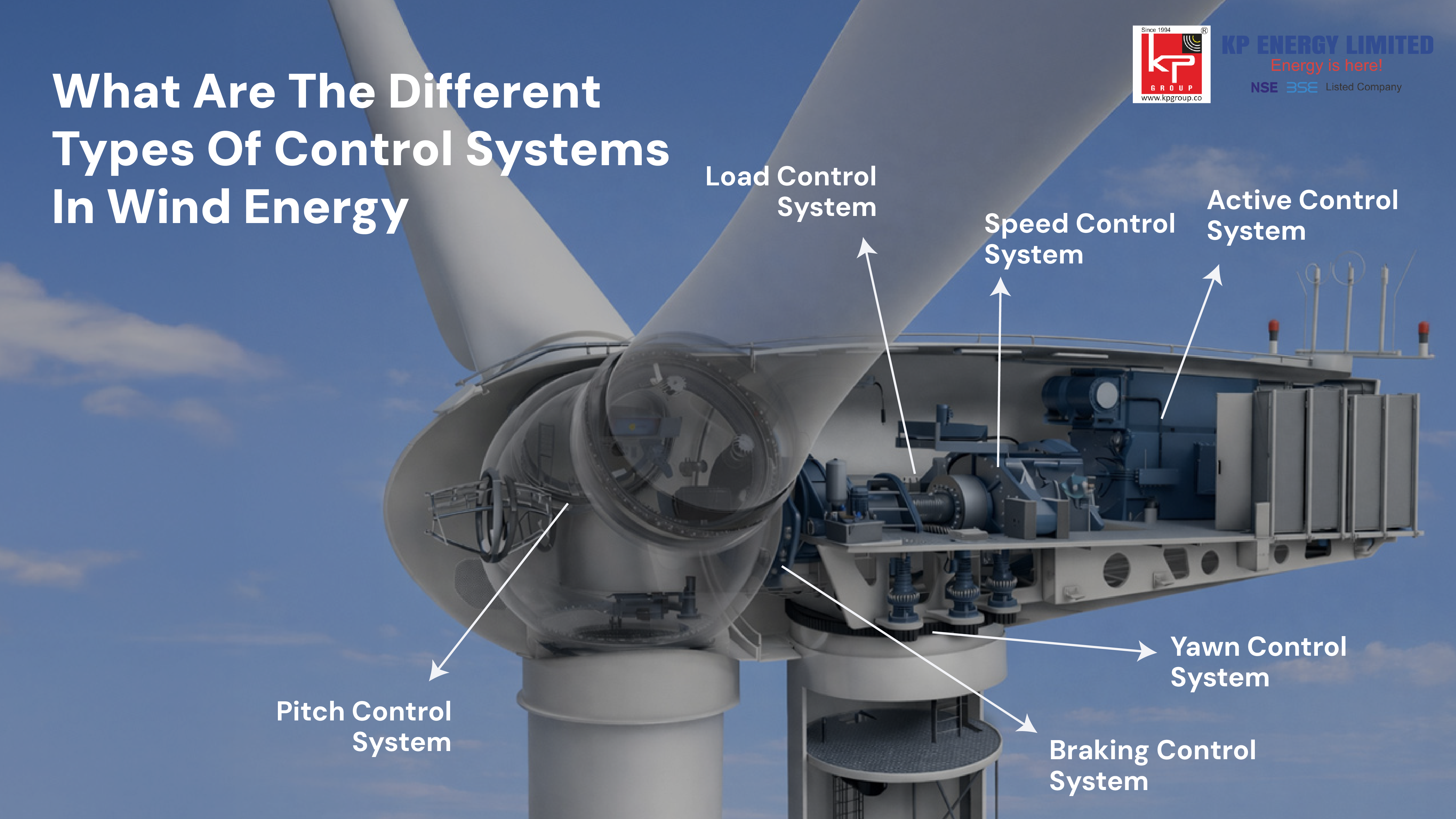
Modern wind turbines employ a variety of control systems, working together in an effort to optimize performance and safety. The main control system in wind energy can be broken down into categories based on their principle of operation, including a number of important key systems.
The most fundamental control systems include:
• Aerodynamic Control Systems: These are responsible for the aerodynamic interaction between the wind and rotor blades and for developing an optimal energy capture method for all wind conditions.
• Electrical Control Systems: These are responsible for the power generation, conversion, and grid integration segment of the system.
• Mechanical Control Systems: These control physical components like nacelle positioning and brake systems
• Safety and Monitoring Systems: These ensure safe operation and provide real-time performance data
• Grid Integration Control: These manage the connection between turbines and the electrical grid
Each of the various systems contains multiple subsystems and components that must work together for best performance from a wind energy conversion perspective. Coupling these control options together involves complex software and hardware solutions that can react quickly to change.
Pitch control in wind turbines is one of the most critical control systems in modern wind energy systems. It adjusts the angle of the rotor blades regarding incoming wind, allowing turbines to maintain the optimum efficiency as the wind speed changes.
The pitch control system operates by rotating the entire blade around its longitudinal axis, changing the angle of attack between the blade and the wind flow. This adjustment serves multiple purposes:
• Power Regulation: At high wind speeds, pitch control reduces the angle of attack to limit power output and prevent turbine overload
• Energy Optimization: At lower wind speeds, the system optimizes blade angles to capture maximum energy from available wind
• Load Reduction: By adjusting pitch angles, the system can reduce mechanical loads on turbine components during extreme weather conditions
• Emergency Protection: In dangerous conditions, blades can be pitched to a feathered position, effectively stopping the rotor
The pitch control system generally comprises electric or hydraulic actuators, and can actively change blade angles in a matter of seconds. Up-to-date systems use algorithms that involve factors that include wind speed and rotor speed and power generation, in order to adjust to what they consider to be the optimal angle of pitch, continuously.
Advanced pitch control systems use individual blade control in which each blade is adjusted independently. That can help reduce the turbulence effects on each blade and reduce fatigue loads, and improve performance of the overall turbine response to complicated wind.
The yaw control system guarantees that the wind turbine is in the best position to capture the maximum energy available from the wind and to protect the turbine from damaging performative loads. The yaw control system operates by rotating the entire turbine nacelle then simply locking the rotor into the vertical position that ultimately, the average direction of the prevailing wind is directed toward the majority of the time.
Key functions of yaw control systems include:
• Wind Tracking: Continuously adjusting nacelle position to follow changes in wind direction
• Load Management: Preventing excessive side loads that could damage turbine components
• Cable Management: Managing the number of rotations to prevent power cable twisting
• Storm Protection: Positioning the turbine to minimize loads during extreme weather events
The yaw system typically consists of multiple electric motors that drive gear systems connected to a bearing ring. Wind direction sensors, usually mounted on the nacelle, provide real-time data to the control system, which determines when yaw adjustments are necessary.
Today's yaw control systems utilize predictive algorithms to predict changes in wind direction and reduce mechanical delay time between wind direction changes and nacelle reorientation. This can improve energy capture and reduce mechanical stress and wear on yaw system components.
Torque control systems and rotor speed control in turbines help manage operating conditions to maximize power production, and provide turbine safety. These systems can provide protection against unstable overspeed conditions that can/could lead to catastrophic failure within the turbine.
The torque control system manages the electromagnetic torque applied to the generator, directly influencing rotor speed. Key components and functions include:
• Variable Speed Operation: Allowing the rotor to operate at different speeds depending on wind conditions
• Power Curve Optimization: Ensuring that the tip-speed ratios always remain within the sweet spot for the maximum energy capture
• Overspeed Protection: Quickly increases generator torque to slow rotor speeds where overspeed conditions is detected
• Grid Synchronization: Ensuring smooth power delivery to the electrical grid
Rotor speed control systems have multiple protective layers. The generator torque for the primary control maintains intended rotor speeds, and the secondary layers generally include pitch control and mechanical brakes for emergency states via aerodynamic braking.
The success of contemporary wind turbines hinges on the ability to interconnect and coordinate several control systems. Each wind turbine control system type must be coordinated and interconnected with one another to maximize performance, as well as safety and reliability.
Load control in wind turbines entails the different methods, or strategies that have been established for the purpose of controlling mechanical loads and stresses that appear in turbine components. These control systems can be vital for increasing turbine life and optimizing turbine performance in complex environments.

Load control strategies include:
• Active Load Reduction: Using pitch control and other active systems to reduce loads during operation
• Passive Load Management: Incorporating design features that naturally limit loads
• Fatigue Load Mitigation: Reducing cyclic loads that cause component fatigue over time
• Extreme Load Protection: Protecting against maximum loads during storm conditions
The use of advanced load control systems necessitates extensive knowledge of the complexities of aerodynamics, structural dynamics, and control theory. Nowadays, virtually all modern turbines feature multiple sensors, making it possible to continuously and instantaneously monitor loads, allowing the control systems to respond rapidly to the wind conditions.
Advanced load control concepts would involve control of individual blades so the pitch can be adjusted individually to limit loads resulting from the blade action, to reduce the local concentrated loading. This approach works exceptionally well to reduce fatigue loads and provide overall better turbine performance in turbulent wind conditions.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems have become essential to the evolving modern wind power plant operational settings by providing monitoring and control capabilities for whole wind farms through centralized systems in their integrated control parameters on each of the turbines.
SCADA systems in wind energy provide:
• Real-time Monitoring: Continuous surveillance of turbine performance and environmental conditions
• Remote Control Capabilities: Ability to control turbines and plant operations from central locations
• Data Analysis and Reporting: Collection and analysis of operational data for performance optimization
• Alarm Management: Immediate notification of equipment problems or abnormal conditions
• Maintenance Scheduling: Predictive maintenance capabilities based on operational data
Nowadays, AI Predictive Maintenance and Machine Learning solutions are increasingly being integrated with SCADA systems in order to detect “creeping changes” in performance that may not result in immediate warnings but are early signs of developing problems that allow for preventive action prior to actual failure.
By bringing together SCADA systems with different types of wind turbine control systems, it creates a complete managing platform that optimizes performance for all turbines on and across the wind farm. These systems have the ability to work together to help optimize turbine operations to reduce wake losses, investigate grid integration needs, and observe real-time market dynamics.
Modern SCADA systems usually also feature advanced analytics and machine learning features that help in predictive maintenance and optimizations (both maintenance and performance) that can significantly improve the economics of wind plants.
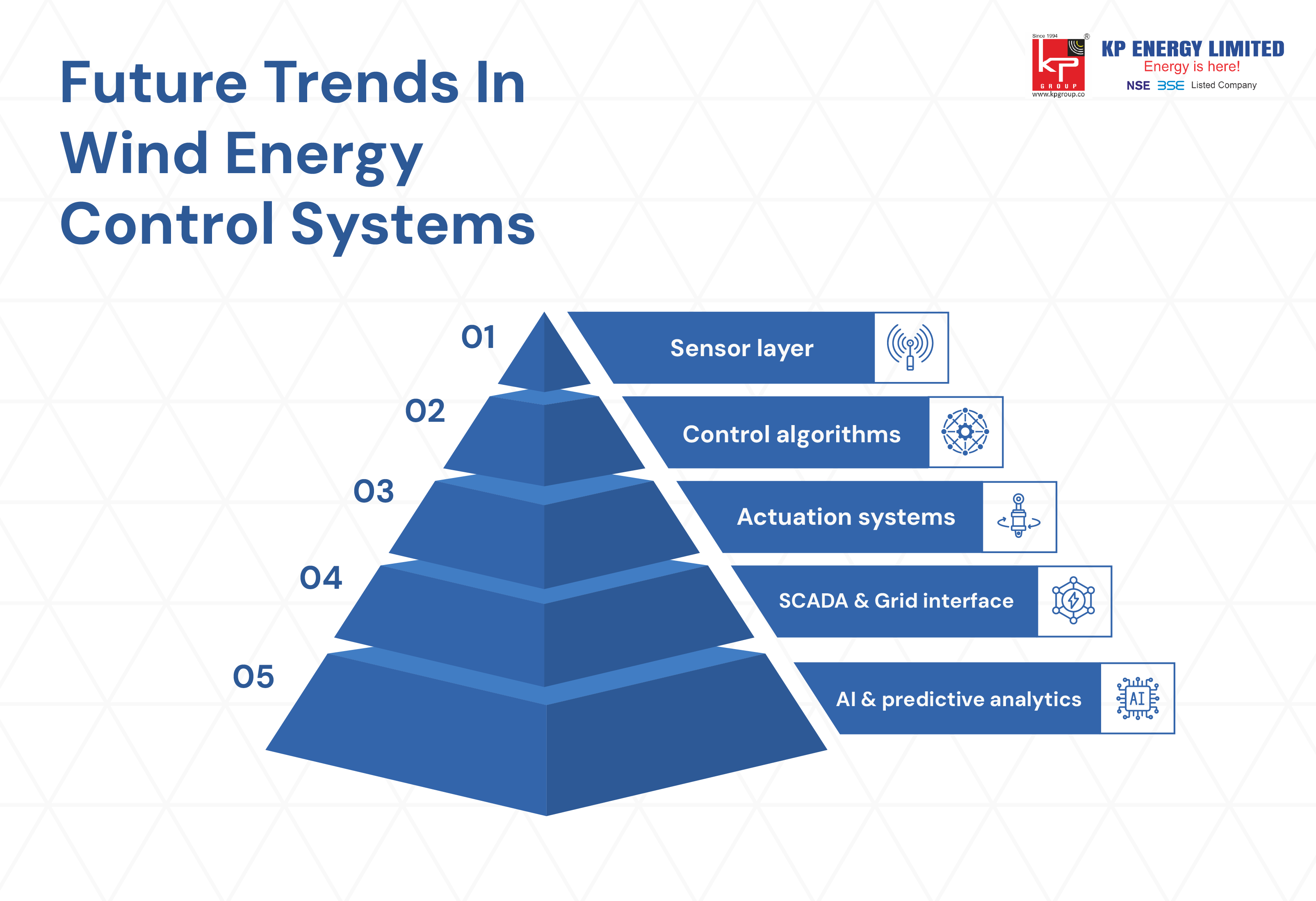
The advancement of control systems and technology in wind energy is still on the rise with the deployment of new technologies that will enhance performance, reliability, and affordability. These new technologies are on the leading edge of developing control systems for wind turbines.
Key advanced technologies include:
• Artificial Intelligence Integration: Machine learning algorithms that improve turbine performance based on both historical data and live conditions
• Predictive Control Systems: Advanced algorithms that predict changing conditions and actively manage turbine requirements
• Distributed Control Architecture: Systems that will distribute the control function over multiple processors to further improve reliability
• Cyber Security Integration: Advanced security measures that strengthen the controls against cyber threats
• Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Enhanced connectivity and data sharing capabilities
AI applications are also being used in turbine control systems, such as radar-linked shutdown systems, which temporarily shut down operation during bird migration seasons to lower the probability of bird collision incidents, thus protecting the environment.
Advanced control technologies are changing the operation of wind turbines. This will have important implications for increased efficiency, reliability, and lower cost with regards to these technologies. The further development of these technologies is another important future aspect of developing wind energy.
The effectiveness of modern wind turbines depends on the seamless integration and coordination of multiple control systems. Each wind turbine control system type must work in harmony with others to achieve optimal performance while maintaining safety and reliability.
System integration challenges include:
• Communication Protocols: Ensuring reliable data exchange between different control systems
• Response Time Coordination: Synchronizing system responses to prevent conflicting actions
• Redundancy Management: Providing backup systems and fail-safe operations
• Performance Optimization: Balancing competing objectives across different control systems
In the case of wind-solar hybrid projects, especially developed by KP Energy, the role of integrated control systems cannot be overstated when it comes to balancing the varying outputs of the two sources in order to improve the stability of the grid.
The coordination of pitch control, yaw control, torque control, etc., requires a sophisticated control architecture, and complicated algorithms. Modern turbines use a more hierarchical structure than traditional control architecture, which allows for conflicting objectives to be addressed in the operating condition and state of the system.
In utility-scale wind projects, this level of control system integration is typically executed under a comprehensive EPC scope of services, ensuring seamless coordination between turbine controls, grid interfaces, and long-term plant performance.
The future of control systems for wind energy will be shaped by technology advancement and ongoing integration with smart grid technology. Additional trends are increased automation, enhanced predictive functionalities, and improved integration with energy storage systems.
Future developments will likely focus on:
• Enhanced AI Integration: More sophisticated artificial intelligence applications for turbine control
• Improved Grid Integration: Better coordination with smart grid systems and energy storage
• Advanced Materials Integration: Control systems that adapt to new turbine materials and designs
• Autonomous Operation: Increased automation and reduced human intervention requirements
• Environmental Adaptation: Systems that better respond to climate change and extreme weather events

Ready to power your business with smarter wind energy systems Connect with KP Energy today.
Q1: What Are The Primary Benefits Of Advanced Control Systems In Wind Energy?
Advanced control systems offer many advantages, such as increased energy production, improved equipment reliability, reduction of maintenance costs, defeating of grid reliability issues, and improved safety. Advanced control benefits the wind plant with energy production gains 5-15% while significantly improving operational costs.
Q2: How Do Control Systems Handle Extreme Weather Conditions?
Control systems respond to severe weather using several mechanisms to protect the machine, some of which will include the automatic shutdown of the turbine, feathering the blades, reorienting the nacelle away from the wind direction, and engaging the mechanical brake systems. These actions will protect the components from damage during severe weather and storms.
Q3: What Role Does Data Analytics Play In Modern Wind Turbine Control?
Data analytics allows for predictive maintenance, optimized performance and operational efficiency. Modern control systems collect large volumes of data regarding operational conditions which can generate data and analytics based on resolved patterns, predict failures, and optimize performance through varying conditions.
Q4: What Are The Main Challenges In Implementing Advanced Control Systems?
Issues can include advanced system complexity, technical integration, cyber security, cost considerations, plus the need for specialized technical knowledge. However, the benefits of deploying advanced control systems outweigh issues in most cases, resulting in advanced control systems increasingly becoming common place in modern wind energy projects.