
The global energy system is undergoing a significant transformation, with a wind energy revolution spearheading the transition to a sustainable future. Countries are struggling with climate change, energy security, and economic development. Wind energy technology is poised to redesign electricity generation and consumption. Wind energy benefits are just not limited to protect the climate but include economic benefit, technological innovation, and social advancement.
This backdrop will explore ten of the most powerful reasons wind energy is leading the renewable energy transition and demonstrate how the clean energy paradigm is transforming power generation and moving the world towards a sustainable future.
Wind energy is the backbone of the transition to renewable energy mainly because of its payback over time, its scalability, and the fact that the technology has "matured". Wind power has unmatched flexibility of deployment across different geography and climate compared to renewables with geographical constraints or issues of constant availability
In many instances, technological advancements have provided grid parity for technology and pricing of the electricity from wind, so that this type of renewable energy can be priced comparable to or equal to fossil fuels. In conclusion, through technological advancements, prices have become economically viable for wind, and are the furthest, most stable base resource for building a sustainable energy supply.
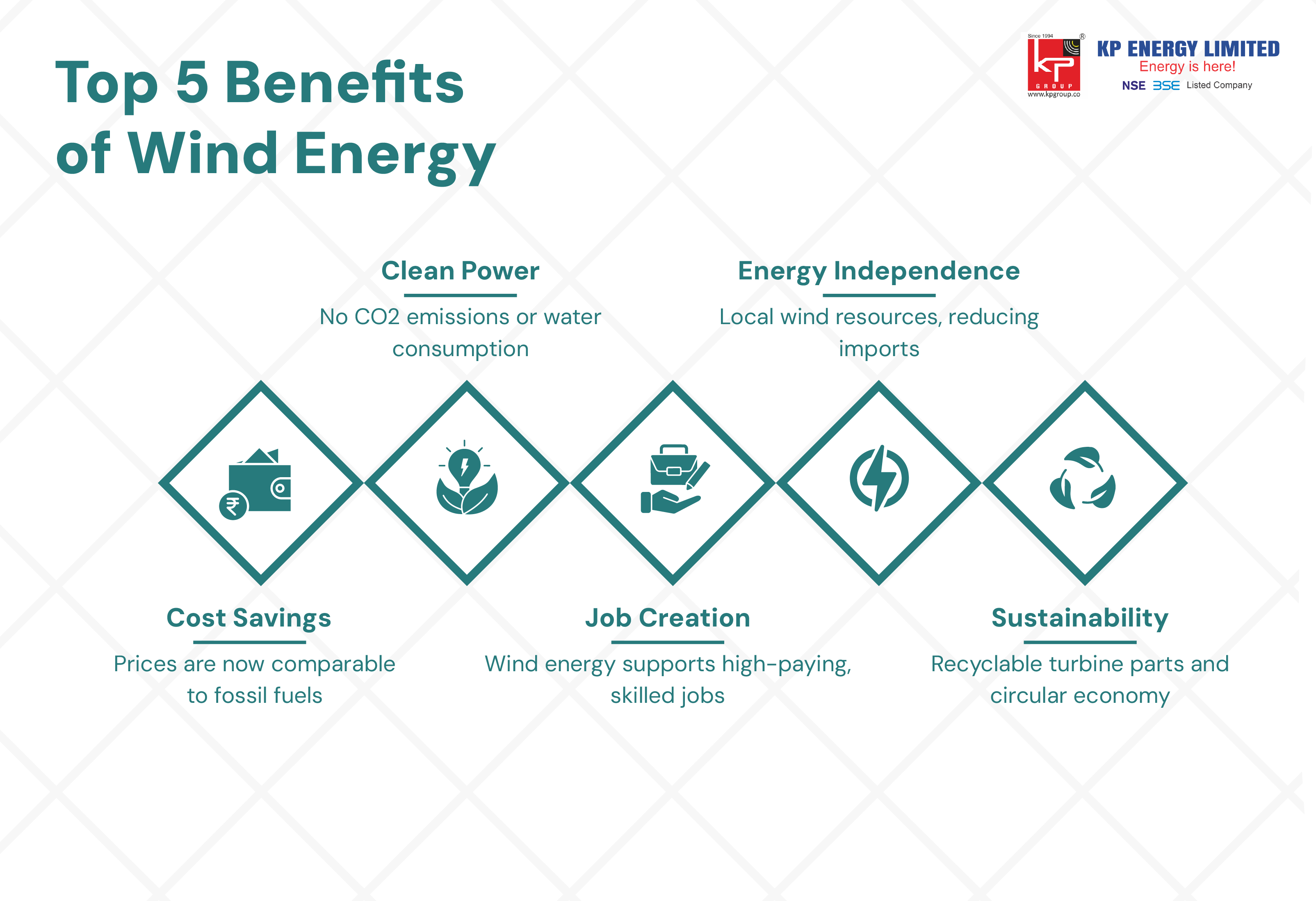
The benefits of wind energy are most evident in its dramatic cost reductions over the past decade. Modern wind turbines and sustainability are inherently linked with efficiencies decreasing the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) to levels never seen before.
Key economic advantages include:
Onshore wind energy costs have decreased by over 70% from 2010 to 2024.
Operational expenses are minimal once turbines are installed
Long-term price stability protects consumers from fossil fuel price volatility
Reduced dependence on fuel imports strengthens energy security
Lower maintenance requirements compared to conventional power plants
The economic transition is particularly impactful in developing economies, where wind provides affordable access to electricity and assists in economic and industrial development, and jobs.
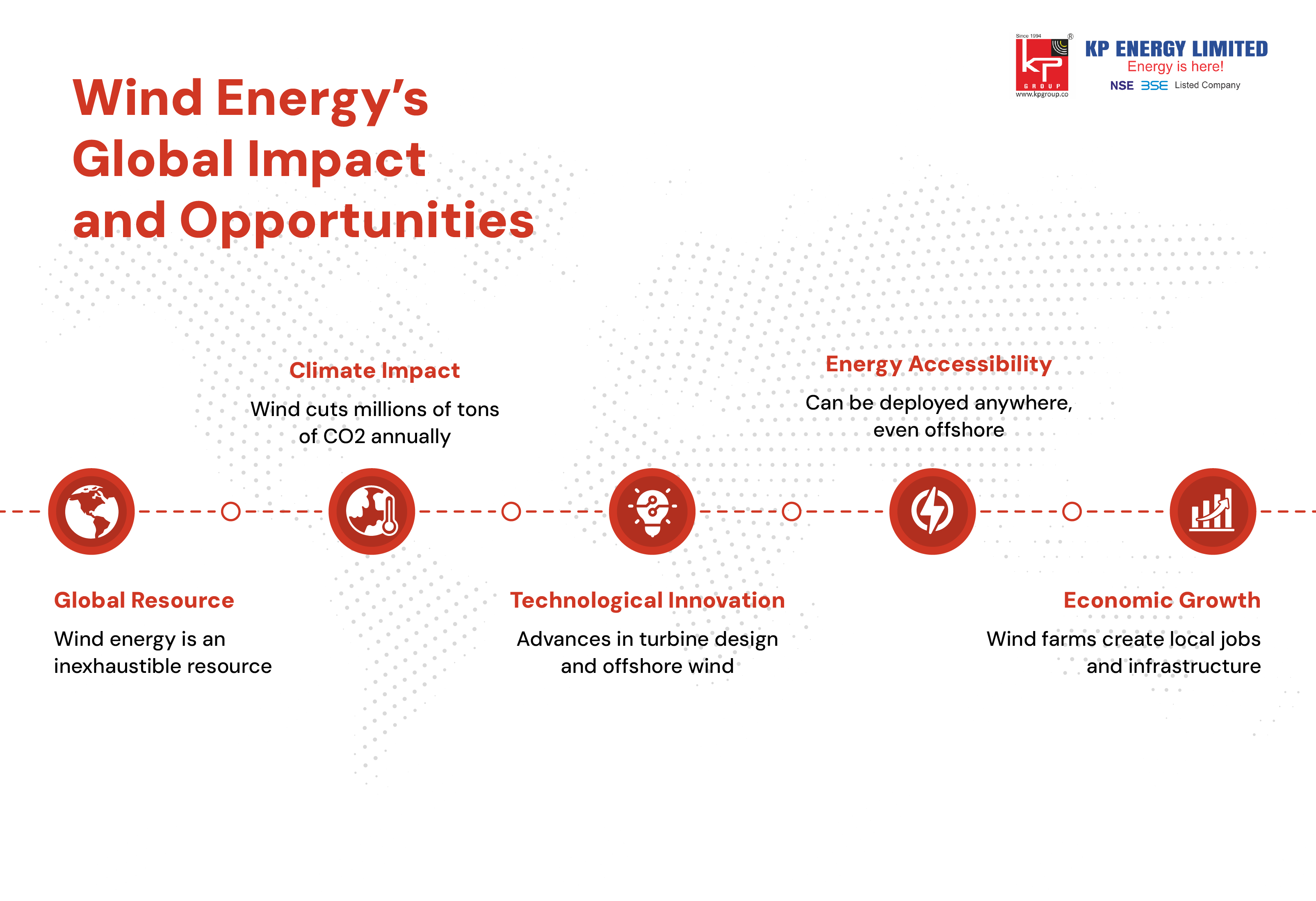
Wind energy revolution represents the greatest opportunity for humanity to avoid climate change through the large-scale decarbonization of the electricity industry. The transition to wind energy comes with intrinsic environmental advantages that are substantial and measurable.
Environmental benefits include:
Zero direct greenhouse gas emissions during operation
Minimal water consumption compared to thermal power plants
No air pollutants or toxic waste generation
Land compatibility with agriculture and livestock
Recyclable turbine components reducing waste streams
In six months of operation, a single modern wind turbine can more than offset its own carbon footprint and will continue to generate zero emissions electricity for approximately 20-25 years. This makes wind one of the most environmentally beneficial pieces of technology on the planet.
The climate benefits of wind energy go beyond just emissions reduction. For every megawatt-hour of wind energy produced, you displace energy generated from fossil fuels, and this has the potential to create a ripple effect on the world's decarbonization for the better.
Wind power's contribution to climate action includes:
Avoiding approximately 300 million tons of CO2 emissions annually
The global community is supported and abiding by commitments established by the Paris Agreement
The holders of carbon emissions are supported as their industries work towards lowering their environmental footprint
Providing clean energy for electric vehicle charging infrastructure
Supporting green hydrogen production for industrial applications
For industries and utilities looking to translate these technological advancements into real-world wind projects, partnering with a comprehensive EPCC scope of services provider ensures efficient execution, regulatory compliance, and long-term project performance.
The evolution of wind technology will be part of the expansion of renewable energy in the future. The design of wind turbines today is an extraordinary example of engineering ingenuity - producing energy while respecting the environment as much as possible.
Technological advancements include:
Larger rotor diameters increasing energy capture efficiency
Advanced materials reducing weight while improving durability
Smart turbine controls optimizing performance in variable wind conditions
Predictive maintenance systems reducing downtime and costs
Grid integration technologies ensuring stable power delivery
Offshore wind technology represents the next frontier, with floating platforms enabling deployment in deeper waters and accessing stronger, more consistent wind resources.
Wind energy revolution increases energy security by reducing dependence on fossil fuel imports and providing energy supplies that can be controlled domestically. This is an added benefit in a world fraught with geopolitical uncertainty.
Energy security benefits include:
Utilization of domestic energy resource decreases reliance on energy imports
Price stability in domestic energy markets from unstable changes in global energy markets
Distributed generation increases grid resilience
Capacity for strategic reserves strengthens national security
Supply chain and transport professional
Wind farms offer economic benefits for rural landowners and communities while being compatible with agricultural land uses.
Wind developments provide rural landowners and communities opportunity while being consistent with existing agricultural use.
Wind energy supports hundreds of thousands of jobs in the manufacturing, installation, operation, and maintenance sectors, many of which provide above-average wages and opportunities to move up in career advancement in rural and industrial community.
Employment opportunities include:
Manufacturing technicians producing turbine components
Installation specialists and construction workers
Operations and maintenance technicians
Engineers and project developers
Supply chain and logistics professionals
The industry's growth trajectory suggests continued job creation, with many positions requiring specialized skills that command premium wages and offer long-term career security.
Wind farms provide significant economic opportunities for rural landowners and communities while maintaining compatibility with existing agricultural activities.
Rural development benefits include:
Lease payments providing stable income for farmers and ranchers
Property tax revenue supporting local schools and services
Construction spending boosting local businesses
Permanent jobs creating population stability
Infrastructure improvements for whole communities
Farmers can still grow crops or graze their livestock in areas near the wind turbines, creating a co-located use of land which maximizes economic value while also improving agricultural sustainability.
The renewable energy transition is being accelerated through the established capacity of wind energy to integrate into current electric infrastructure while providing greater reliability and predictability of power generation.
Present day wind energy systems utilize advances in technology that enhance electrical grid stability and reliability, not hinder them.
Grid integration advantages include:
Advanced forecasting systems predicting output 48-72 hours ahead
Rapid response capabilities supporting grid frequency regulation
Distributed generation reducing transmission losses
Energy storage integration smoothing power delivery
Smart grid compatibility enabling demand response programs
These capabilities make wind energy a valuable grid asset rather than a burden, contributing to overall system efficiency and reliability.
The Benefits of wind energy are high degree of scalability from small community projects to large utility scale projects, creating deployment flexibility across a variety of economic and geographical contexts.
Deployment advantages include:
Modular construction allowing phased development
Rapid installation timelines compared to conventional power plants
Site flexibility accommodating various terrain types
Capacity expansion possibilities as demand grows
Technology standardization reducing project risks
This scalability makes wind energy accessible to developing nations while supporting continued growth in mature markets.
The future of renewable energy will be related to technologies that can accommodate growth in global electricity demand meanwhile ensuring environmental sustainability and economic sustainability for decades.
Wind is an essentially unlimited energy source that will continue to be available as long as the sun continues to heat the Earth's atmosphere and creates weather patterns.
Resource advantages include:
Inexhaustible energy source requiring no fuel inputs
Global resource distribution enabling worldwide deployment
Predictable seasonal and diurnal patterns supporting planning
Technology improvements accessing previously unusable wind resources
Ocean wind resources providing enormous expansion potential
The International Energy Agency estimates that wind resources could theoretically supply all global electricity demand many times over, ensuring long-term energy security.
Wind turbines and sustainability work neatly into the principles of a circular economy, which focuses on keeping efficiencies related to resources, waste, and recycling materials during the life cycle of technology.
Sustainability features include:
Recyclable materials comprising 85-90% of turbine mass
Steel and concrete foundation materials fully recyclable
Composite blade recycling technologies under development
Minimal water and chemical usage during operation
Land restoration capabilities after project decommissioning
The industry is working to create closed-loop recycling systems that will eliminate waste completely and improve resource efficiencies.
Q1: What Makes Wind Energy More Reliable Than Other Renewable Sources?
Wind energy benefits from a combination of technology, forecastability of resources, and interoperability with the grid that can be more reliable than near all the other renewable energy sources. The wind energy industry's advancements in forecasting actually allows us to forecast wind generation out to 48-72 hours. Furthermore, the geographic reliability and integration with storage infrastructure, all contribute to potential increased reliability in wind generation.
Q2: How Does Wind Energy Impact Local Wildlife And Ecosystems?
Wind energy installations are built today with comprehensive environmental assessments, wildlife visioning, and wildlife protection plans.. While birds and bats may be impacted, the impacts are much lower than what is caused by fossil fuel generation, other structures, vehicles, and outdoor pets (e.g. cats). Wind turbine site assessments explicitly assess migration paths, and technological advances are allowing radar to be used to monitor peaks during migration seasons, as well as when a turbine may be temporarily shut down to limit impacts to birds and bats from the turbine.
Q3: What Happens To Wind Turbines At The End Of Their Lifespan?
Generally, wind turbine life is about 20-25 years, after which they are generally shut down and taken down. The wind turbine parts made from steel towers, concrete foundations, and copper cable can all be recycled (100 recyclable).The wind industry is working to innovate and develop recycling technologies that are designed specifically for composite wind turbine blades. Additionally, several companies have shown the capability of reusing fiberglass materials from blades in a reversible manner for use in cement and other products after they've reached the end of their life cycle as wind turbine blades.
Q4: Can Wind Energy Meet All Global Electricity Needs?
The research finds that, in a global context, wind is the an important resource to meet electricity demand while also finding that a long-term 100% renewable electricity system, at lower costs, is an a good renewable energy plan, which includes or supplements wind with solar and hydro power, and adds in storage technologies and improved electric grid capacity. Wind may provide about 30%-50% of global electricity demand in a 100% renewable scenario.
Q5: How Does Wind Energy Perform In Extreme Weather Conditions?
Modern wind turbines are designed for extreme weather events - hurricanes, ice storms, extreme temperatures, etc. Wind turbines are equipped with automatic shut down systems that turn off the equipment during dangerous conditions, and cold-weather packages that allow them to operate in sub-arctic environments. Offshore turbines are designed to withstand marine conditions and severe storms, and offshore turbines have been seen to perform better than coastal infrastructure in extreme weather events.