
People know about how we generate electricity from renewables as we head towards a cleaner, renewable energy future. Electricity is generated from renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydro power generation. These renewable energy systems are reshaping our energy landscape in how we use energy in our homes, cities, and modern industries.
In this guide, we intend to explain the different types of renewable energy sources in conjunction with the renewable energy electricity generation process and show how solar panels generate electricity and how hydroelectricity power works.
The clean energy generation concepts are focused on generating electricity in a form that does not adversely affect our environment. Renewable energy will be pollutant-free because it utilizes solar, wind, and water i.e., the natural processes that do not create carbon emissions (wastes).
Let’s understand the difference between what renewable vs non-renewable energy really means.
Renewable energy is obtained from natural sources that are present in abundance like sunlight or rivers. Such resources are used to make electricity, as they can never run out.
On the other hand, non-renewable energy comes from things like coal and oil, which take millions of years to form. Once we use them up, they’re gone, and they cause a lot of pollution if they are being used.
Switching energy generation sources from fossil fuels to renewable energy is not just beneficial to the planet. It is an excellent strategy for present and future economic growth and energy security.
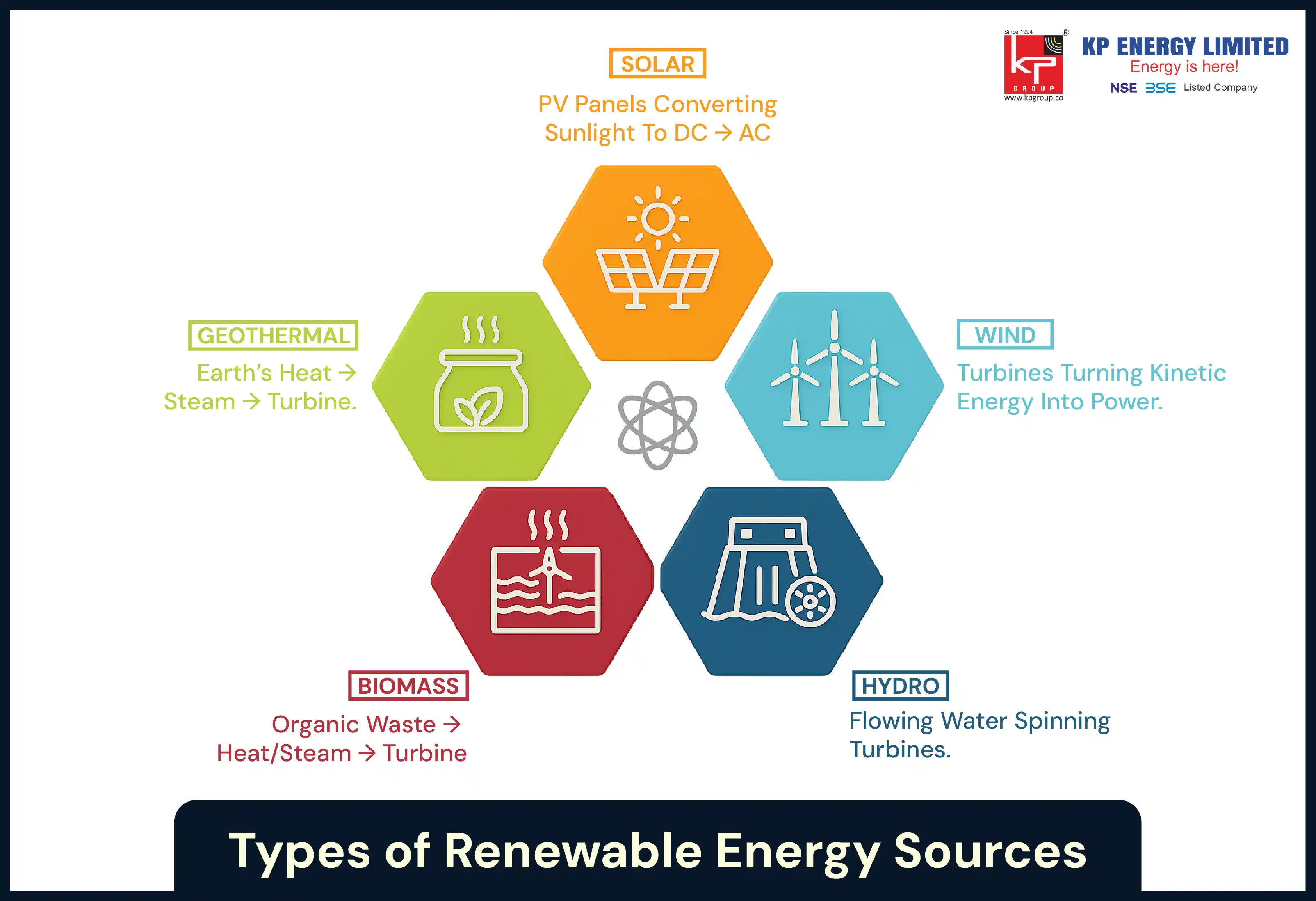
Now, we should examine the different types of renewable energy sources and how each one works in the energy generation system.
First up, as far as clean energy technologies go, solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, converting sunlight into electricity is the most understood process. PV cells absorb solar radiation and turn it into direct current (DC). In the end, an inverter converts the direct current to alternating current (AC), which is suitable for homes and industry.
Wind energy electricity generation involves turbines that rotate when wind passes over their blades. The kinetic energy of wind is converted into mechanical energy. This mechanical motion spins a generator, creating electricity.
Offshore and onshore wind farms are vital in countries like India, Germany, and Denmark.
As a major part of green energy generation methods, wind power is scalable and efficient.
By learning the mechanics of hydroelectric power is really quite beautiful as a historical form of production.
Water is diverted into a reservoir, which is released from the reservoir through turbines. The pressure and moving water rotate the blade of the turbine, which spins the generator.
The generation of electricity in this method has an incredibly high efficiency, generating more than 90% of the energy supply.
Hydropower is ultimately the biggest means of renewables for electricity generation, due to its capability of consistently producing electricity.
Biomass is where we utilize plant and animal waste to create heat and electricity. For example, agricultural residues, wood chips, and the food suppliers, food waste, and municipal waste could be burned or digested. The heat produced creates steam that spins a turbine.
This is one of the few forms of generating green energy that also resolves the waste issue by eliminating waste.
Geothermal plants utilize underground reservoirs of steam and hot water. The natural heat in the reservoirs is pulled to the surface to rotate the turbine.
While reliable in generating output, geothermal has limited geographic locations. Still, the sustainable electric sources will continue to be strongly utilized in countries such as Iceland, Kenya, and the Philippines.
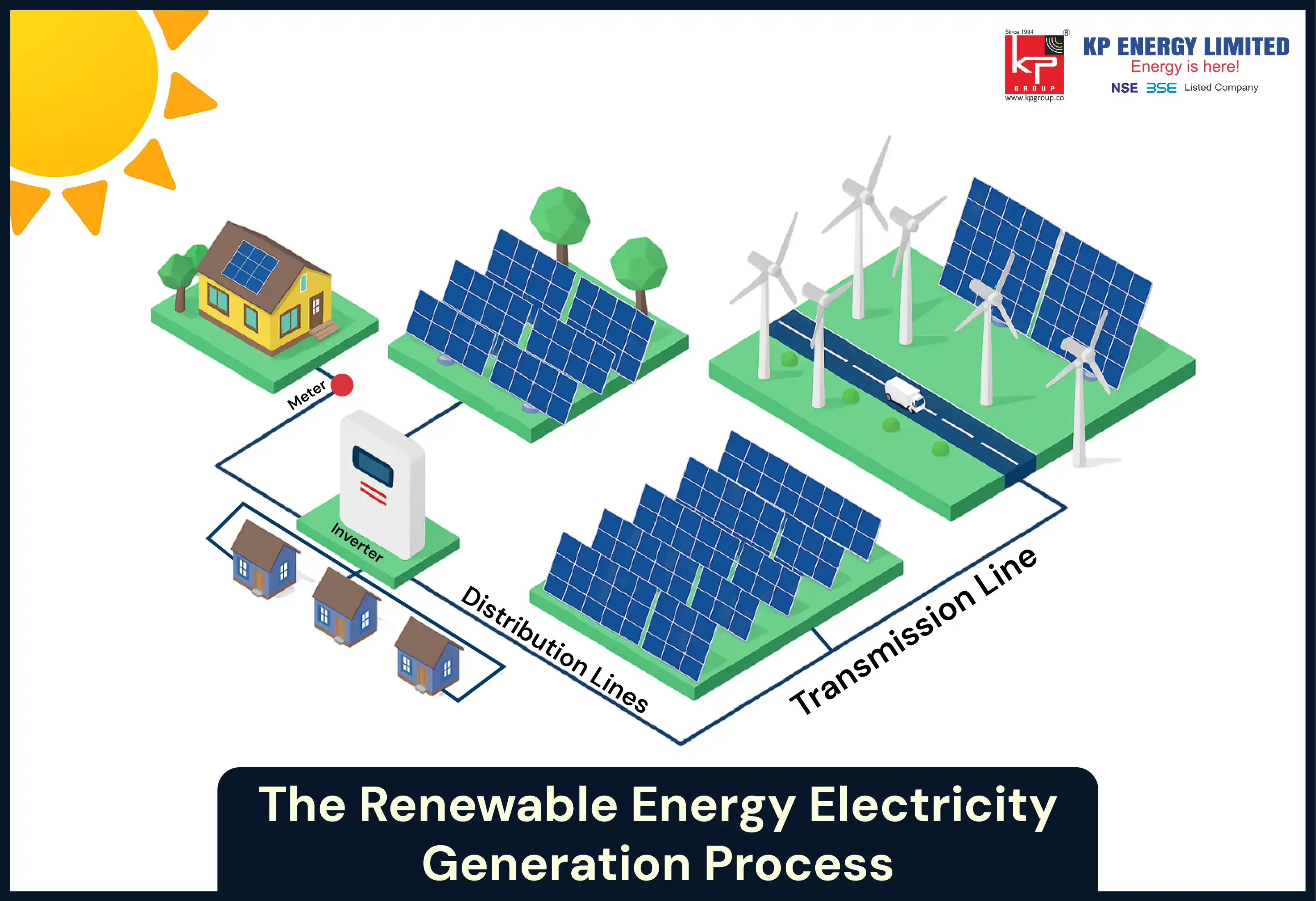
Regardless of the source, the core steps in the renewable energy electricity generation process are the same:
Capture a natural resource (sunlight, wind, water, etc.)
Convert it into mechanical energy (motion, pressure, or heat).
Transform it into electrical energy using generators.
This process ensures minimal emissions and increases efficiency through modern technologies like smart grids and battery storage.
These three forms dominate modern clean energy power generation:
Modular: can be deployed at any scale.
Low operating costs after installation.
Works well in remote and urban areas.
Ideal for coastal and open plain regions.
Can be integrated with battery storage.
Reliable and continuous power generation.
Great for peak load balancing.
Long lifespan of infrastructure.
Together, solar, wind, and hydro power generation form the backbone of most national renewable energy programs.
All green energy generation methods drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other air pollutants. They help to prevent global warming effects in the atmosphere they also conserve diversity.
Wind and solar technologies' costs have fallen by more than 80 % in the last 10 years. Since natural resources are free to use, the bulk of operating costs are not significant.
Implementing renewable electricity supply sources decreases reliance on imported fossil fuels and protects countries around the world from fluctuations in global fossil fuel prices.
Countries all over the world are demonstrating that the way electricity is generated from renewable energy is infact, scalable:
China is the global leader in hydropower and solar capacity.
Germany, with limited sun, is number two in solar generation, supported by strong policy support.
India is one of the most rapidly developing places for wind energy electricity generation development, in which states like Tamil Nadu and Gujarat are leading the way.
Antarctica, a remote continent unsurprisingly, is also deploying wind turbines to provide electricity to its research stations.
These countries are showing that investments in clean energy, supported through innovation and policy alignment, can scale clean energy power generation across the world.
Despite its potential, there are challenges in the adoption of green energy generation methods :
Intermittency: Solar and wind depend on weather conditions.
Storage: Reliable battery systems are needed to ensure round-the-clock power.
Grid Integration:Traditional grids must adapt to handle decentralized inputs.
Ongoing innovation in storage and smart grid technologyis helping bridge these gaps.
The future of energy is about forming generation electricity using renewable energy. More broadly, it includes the infrastructure of electrical grids, also storage. Not only is the direction possible, but the decrease in costs, various policy favorable factors, and tech innovation it inevitable.
Whatever knowledge we have, from wind-generated electricity to how hydropower works, takes us to a greener future and a cleaner environment for future generations.
Q1: What is the Most Common Renewable Energy Source Globally?
Until recently, hydropower was considered the most common renewable energy source in the world because of its long-standing history, large-scale dams, and the highest installed capacity. However, recent trends show a significant shift, when combined, solar and wind energy have now surpassed hydropower in terms of overall electricity generation.
This change has been driven by rapid technological advancements, declining installation costs, government support, and the ability of solar and wind to be deployed quickly across diverse geographies.
Q2: Can Solar, Wind, and Hydropower Generate All the Energy the World Needs?
Yes! If we put enough money into building all the types of government infrastructure systems, these types of electricity produce enough green delivered electricity to provide for the world's energy needs.
Q3: Why is understanding the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy necessary?
Knowing the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy will help people to be better informed to make better choices about sound policies, clean energy investments, what type of "home" energy to use, and which appliances to purchase. It is about realizing sustainability is a lifestyle choice instead of investing in limited resources that are infinitely destroying the planet.