
In the electricity intensive industrial landscape today, having an accessible, reliable and low-cost power supply is crucial for uninterrupted operations in industrial environments. Even though grid electricity is considered the standard power supply for most industries, there are a lot of industries that are increasingly implementing ways in which captive power plants can run more effectively. This is being done to achieve cost savings and attain energy independence. In business, captive power plants simply refer to a facility that provides a source of electricity that the industry generates for its use, rather than being fully dependent on the electricity sourced from the state electricity grid.
This article will explain what is captive power plant, its importance, the different types, the benefits of captive power plants for industries, how it fits into the electricity grid-based power, the captive power policy in India, renewable-based captive projects, such as captive solar power plants for factories, and whether self-generation allows for industrial energy management solutions.
A captive power plant (CPP) is a power generation facility installed by an industry or a group of industries to meet their own electricity needs for different requirements, including manufacturing, operation, and auxiliary processes. The main advantage of setting up a captive power plant (CPP) is to ensure a constant, uninterrupted energy supply at the most optimized cost.
Self-generation of electricity in industries for their consumption.
It can be established by a single industrial unit or a consortium of companies.
Can operate on diverse fuel sources such as solar, wind, natural gas, or biomass.
Reduces dependency on the grid and ensures stable operations even during outages.
Often integrated with industrial energy management solutions for better monitoring and optimization.
Industries have an option to choose from different types of captive power plants. The choice is dependent on various factors like their scale, fuel availability, and sustainability goals.
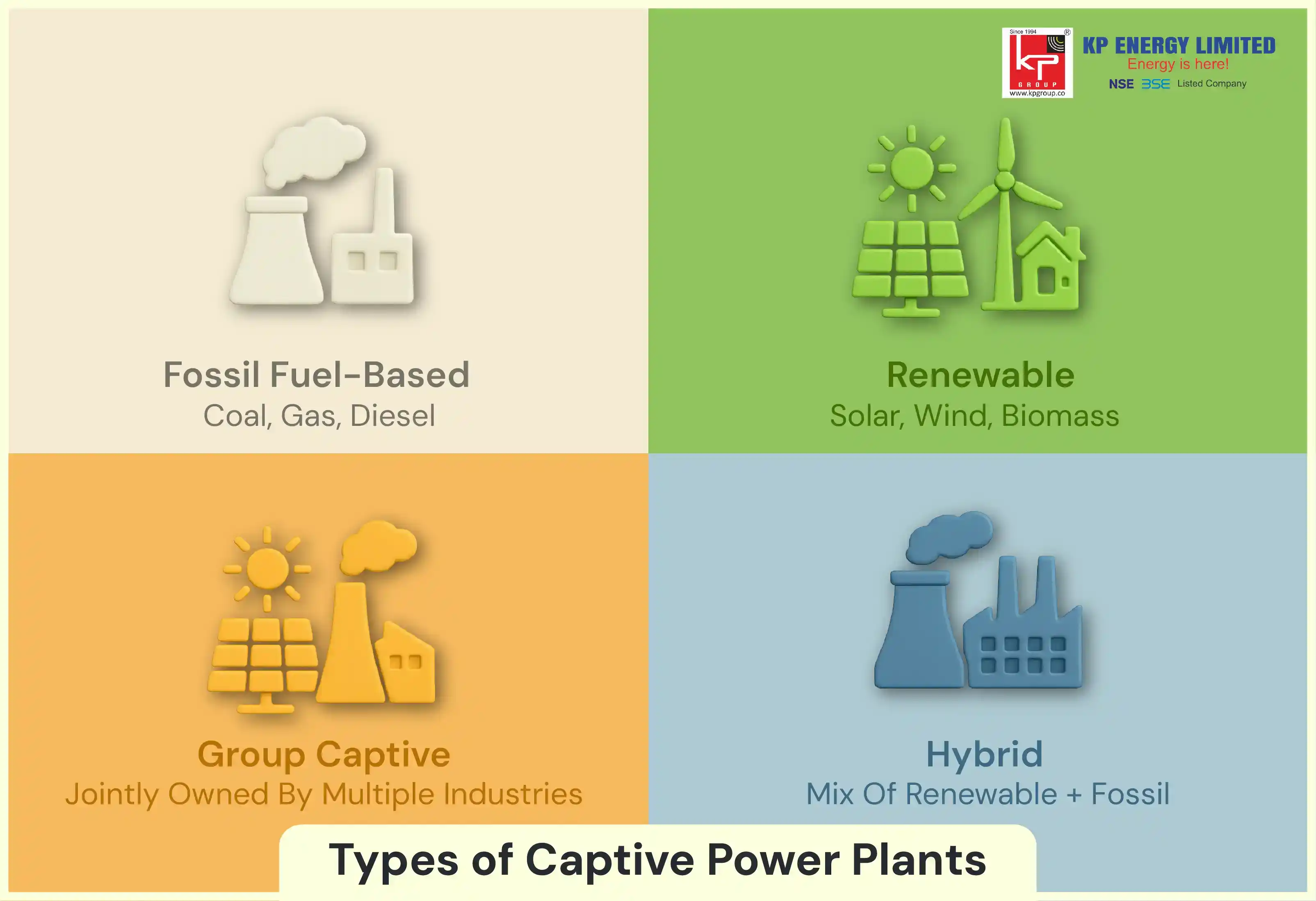
These operate using coal, diesel, or natural gas.
It is apt for industries where energy requirements are high, like steel, cement, or textiles.
These plants are worth it in providing reliable, large-scale power. However, they face challenges of rising fuel costs and environmental concerns.
Captive solar power plants for factories are becoming increasingly popular. The major reasons for this are two: low operational costs and government incentives.
Biomass and wind-based captive plants are also an option and can be used where resources are abundant.
These support the long-term sustainability goals and also help in reducing carbon emissions.
Combine fossil fuel and renewable sources to balance reliability and cost efficiency. One instance of this could be any industry utilising a mix of solar+wind, solar + gas, or solar + biomass systems.
These are set up by multiple industrial consumers. They collectively invest in the plants and consume the power as per their needs.
Provides scale benefits and makes renewable adoption more viable.
A common debate in industrial energy management is captive vs grid power. While grid power is accessible, industries often face challenges like fluctuating tariffs, transmission losses, and outages.
Reliability: Reduces exposure to power cuts and voltage fluctuations.
Cost Control: Industries can optimize fuel mix and save on rising grid tariffs.
Energy Security: Ensures a consistent supply for critical processes.
Flexibility: Ability to integrate renewables and hybrid models.
The benefits of captive power plant for industries are not just limited to cost savings. Multiple strategic advantages directly influence competitiveness and operational efficiency, which ultimately make people opt for these.
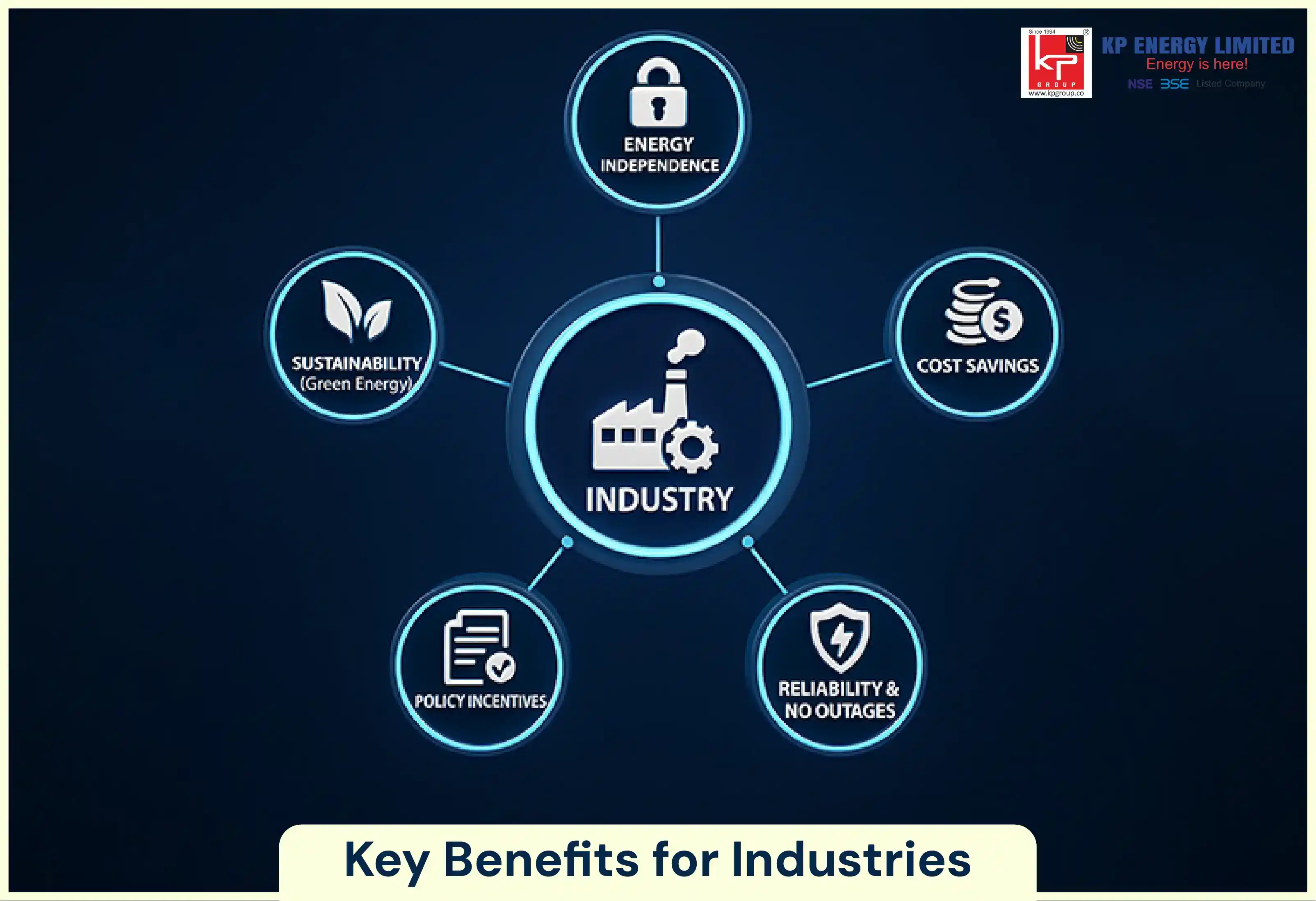
Grid tariffs are often high and unpredictable, and these reduce dependency on them.
It helps avoid transmission and distribution losses.
Provides a stable, long-term, and cost-effective structure, especially with renewables like solar, wind, and many more.
Prevents production losses during grid outages.
Offers voltage stability for industries where precision machinery is involved.
Industries get multiple incentives under the captive power policy in India. These include exemptions on cross-subsidy surcharges for captive users, which is a huge benefit.
Encourages investment in self-generation, lowering the burden on the grid.
Installing a captive solar power plant for factories helps industries cut emissions. It also helps them align with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
It supports the cause of long-term reduction in carbon footprint and enhances global competitiveness.
CPPs integrate seamlessly with industrial energy management solutions. This allows better monitoring, automation, and efficiency.
Hybrid models balance renewable and non-renewable sources.
The financial advantage of captive generation is one of the strongest drivers for adoption.
Lower Cost Per Unit: Generating electricity on-site often costs significantly less than buying from the grid.
Avoiding Penalties: Industries can prevent penalties for exceeding sanctioned demand.
Optimized Tariff Structures: Group captive and renewable-based systems provide predictable energy expenses.
Long-Term Savings: Captive solar power plant for factories offers savings for 20–25 years with minimal maintenance costs.
The captive power policy in India is governed under the Electricity Act, 2003. It is also governed by subsequent regulations issued by state and central authorities.
For a power plant to qualify as captive, at least 26% ownership must be held by the captive user(s). Additionally, 51% of the power generated must be consumed by them.
Captive users are exempt from paying cross-subsidy surcharges and additional surcharges that are applicable to open access consumers.
Policies increasingly support renewable-based captive projects through accelerated depreciation, tax benefits, and net metering provisions (where applicable).
These regulations make industrial captive power generation a highly attractive solution for companies seeking energy independence and cost stability.
Among the various options, captive solar power plants for factories has gained significant momentum due to falling solar costs and favorable policies.
Factories with high daytime loads, such as textile, automobile, and pharmaceutical units, derive maximum benefits from solar-based CPPs.
To maximize returns, industries integrate CPPs with industrial energy management solutions that provide:
Real-time energy monitoring and analytics.
Load forecasting and optimization.
Automatic switchover between captive and grid supply.
Performance benchmarking of renewable assets.
This integration helps industries not only reduce costs but also align with digital transformation strategies.
The emergence of captive power plants has changed the way industries in India are going to meet their growing energy demands. With the ability for industries to self-generate, captive power plants (CPP's) create opportunities for cost savings, daily operational stability and sustainable options. Captive power plants give industries options in producing power using fossil fuel, renewable, or hybrid systems, and allow fast implementation of projects that support industries wanting to reduce their dependence on grid supply and to create autonomy in energy generation and consumption for the future. With an incredibly favorable captive power policy in India, and the transition to captive solar power plants for factories, industrial energy independence is here to take off.
For industries already on the path of improving energy security while lowering costs of operations, investing in industrial captive power generation is not an option but a strategic opportunity. KP Energy provides end-to-end captive power solutions, enabling industries to achieve reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable energy independence. Backed by strong engineering capabilities and a proven track record in large-scale renewable projects, KP Energy ensures faster project implementation, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational efficiency for industrial clients.
Q1. What is a captive power plant?
A. A captive power plant is a power-generating facility established generally by an industry or even a group of industries for generating electricity mainly for self-use instead of depending on the state electricity grid.
Q2. What are the types of captive power plants?
A. The major categories of power plants include fossil fuel-based, renewable-based (solar, wind, and biomass), hybrid designs, and group captive power plants.
Q3. What are the benefits of a captive power plant for industries?
A. The main advantages of a captive power plant for industries are cost savings and reliability. Alongside consistency, exemption from cross-subsidy charges, sustainability through renewables, and improved flexibility to manage energy also contribute to the shift of people choosing this.
Q4. How does captive vs grid power compare?
A. Captive power is more reliable, cost-effective, and flexible compared to grid power. Grid power is subject to outages, rising tariffs, and transmission losses.
Q5. Can industries install captive solar power plants?
A. Yes, absolutely! Industries can easily set up captive solar power plants. This will eventually help generate clean energy at lower costs. Additionally, this ensures long-term savings and compliance with sustainability goals.